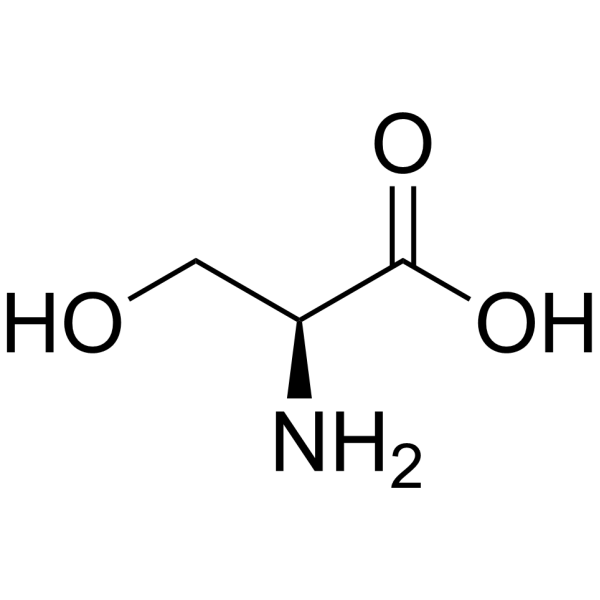
Serine
26,018 views
Amino Acids
- Serine
- Asparagine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- Methionine
- Proline
- Glycine
- Threonine
- Cysteine
- Tyrosine
- Glutamine
- Aspartate
- Glutamate
- Histidine
- Lysine
- Arginine
Summary
Serine, which abbreviates to the 3-letters Ser or one-letter S, is one of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins in our body. Serine’s R-group is a hydroxymethyl group; that is, an alcohol attached to a single bridging carbon. Because of its hydroxyl group, serine can be phosphorylated; in fact, it is the amino acid most likely to be phosphorylated in our body. Serine is also a polar, hydrophilic amino acid, with a neutral charge at physiological pH.
Key Points
- Serine
- Abbreviations
- Ser, S
- Chemical Structure
- R-Group: -CH2-OH
- 1 bridging methylene β carbon (-CH2-)
- Contrast vs. Threonine (which has a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon)
- Hydroxy group
- Phosphorylatable by serine kinases
- Serine is the amino acid most likely to be phosphorylated
- 1 bridging methylene β carbon (-CH2-)
- Polarity
- Polar (water soluble/hydrophilic)
- Charge at pH 7
- Neutral (0)
- Abbreviations