Tyrosine
3,809 views
Amino Acids
- Serine
- Asparagine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- Methionine
- Proline
- Glycine
- Threonine
- Cysteine
- Tyrosine
- Glutamine
- Aspartate
- Glutamate
- Histidine
- Lysine
- Arginine
Summary
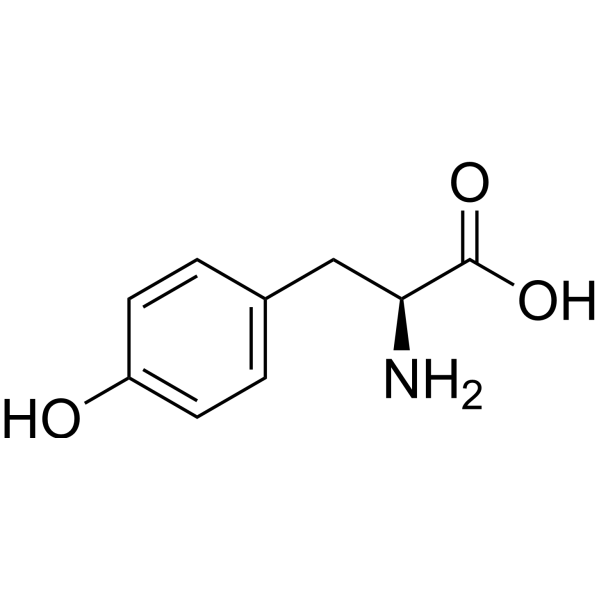
Tyrosine is an amino acid abbreviated as the 3 letters Tyr, or the single letter Y. Its R-group consists of 1 carbon linkage to a phenol group, which is just an aromatic benzene ring with a hydroxyl or alcohol group attached to it. The hydroxyl group makes tyrosine polar or hydrophilic, meaning that it can dissolve in water. The hydroxyl group also reacts with phosphate, meaning tyrosine is one of the most commonly phosphorylated amino acids. Tyrosine is neutral or uncharged at physiological pH and it serves biologically as a precursor to many important hormones, including epinephrine and thyroid hormone.
Key Points
- Tyrosine
- Abbreviations
- Tyr, Y
- Chemical Structure
- R-group: -CH2-phenol
- Aromatic benzene ring
- Aromatic compounds absorb UV light
- Hydroxy group (-OH)
- Phosphorylatable
- Usually performed by tyrosine kinases; serve key steps in cell signaling (e.g. RTKs) and other functions
- Aromatic benzene ring
- Polarity
- Polar (water soluble/hydrophilic)
- Charge at pH 7
- Neutral (0)
- Other Information
- Precursor to catecholamines (e.g. Epinephrine) and some hormones (e.g. Thyroid Hormones)
- Abbreviations