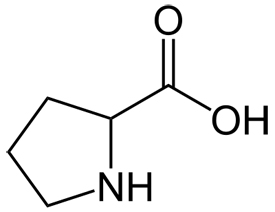
Proline
4,030 views
Amino Acids
- Serine
- Asparagine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- Methionine
- Proline
- Glycine
- Threonine
- Cysteine
- Tyrosine
- Glutamine
- Aspartate
- Glutamate
- Histidine
- Lysine
- Arginine
Summary
Proline, which abbreviates to the 3-letter Pro or single letter P, is one of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins in our body. Proline’s R-group is unique in that it bends backwards on itself to connect with the amino group attached to the core or alpha carbon. This forms a 5-sided ring-shaped R-group incorporating the nitrogen of this amino group. Due to the rigid, ring-shape of this R-group, proline causes kinks in any polypeptide chains that include it. Proline is also a non-polar, hydrophobic amino acid, with a neutral charge at physiological pH.
Key Points
- Proline
- Abbreviations
- Pro, P
- Chemical Structure
- R-Group: 4-C chain forms 5-membered ring with nitrogen of amino group
- Hydrogen of nitrogen unaccessible for forming H-bonds in polypeptide chains
- Kinks polypeptide chain
- Conformational rigidity of amino group in amide bond connecting amino acids in polypeptide chain causes bends
- Disrupts secondary structures like alpha-helices or beta-pleated sheets (rarely occurs in those structures)
- Often found in joining regions between secondary structures
- Polarity
- Nonpolar (lipid soluble/hydrophobic)
- Charge at pH 7
- Neutral (0)
- Abbreviations